
Table of Contents
An Overview of Industrial Internet of Things and Smart Factories
The notion of “smart factories,” in which digital technology and interconnected systems and machinery operate in harmony, has emerged as a result of recent developments in industry. Important to this shift is the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), a subset of the larger Internet of Things (IoT) environment designed with industrial applications in mind. Through the use of the Industrial Internet of Things, sensors and machines in factories are able to exchange data in an effortless manner, allowing for the optimization of safety, productivity, and efficiency.
The ideal factory of the future would be a “Smart Factory,” which would allow for infinitely variable production thanks to data-driven insights, automation, and digitization. In view of sustainability targets, increasing energy prices, and climate change concerns, energy efficiency is becoming an increasingly important aspect of smart factories. Industrial Internet of Things integration allows smart factories to significantly improve overall performance while reducing energy consumption.
The Importance of Industrial IoT for Smart Manufacturing
Using the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT):

Sensors and gadgets in a smart factory gather data in real-time from various sources, including machinery, production lines, and environmental factors. Advanced analytics assist decision-makers obtain insight into factory operations from this data that is delivered to a centralized system. In order to detect inefficiencies, save downtime, and avoid expensive equipment failures, real-time monitoring is highly beneficial.
Predictive Maintenance:
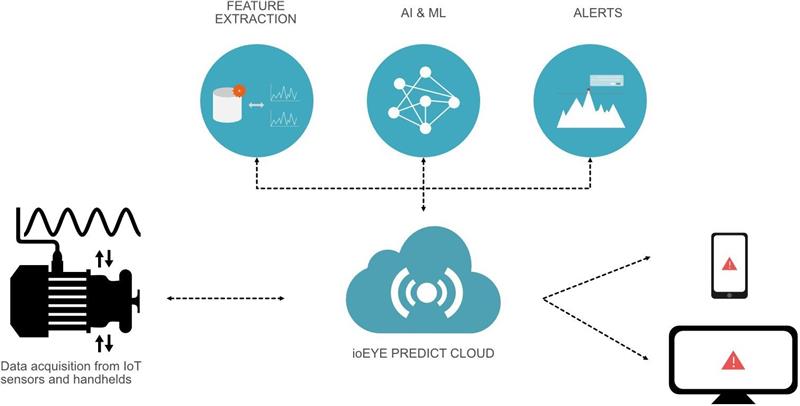
Among the many potential uses for the Industrial Internet of Things, predictive maintenance stands out as particularly encouraging. Predictive algorithms can foretell breakdowns by detecting early indications of wear and tear through sensors implanted in industrial equipment. That way, manufacturing facilities may cut down on energy loss from things like broken machinery and needless idle.
Remote Management and Control:

Manufacturers are now able to remotely supervise and control manufacturing activities thanks to the IIoT. From a single dashboard, managers can keep tabs on many factories in different locations, tweak machine settings, and maximize energy efficiency. Businesses can cut down on energy use and operational expenses by lowering the requirement for on-site interventions.
Improving Smart Factory Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency has risen to the forefront as a key concern for enterprises aiming to decrease their carbon footprints. Lighting, HVAC, lighting, and machine operation are just a few of the traditional manufacturing activities that use a lot of energy. Smart factories that use the Industrial Internet of Things can monitor their energy consumption in real time, which helps industries save money and reduce waste.
Energy Tracking and Efficiency Enhancement:

Machine and system energy usage can be monitored with IIoT-enabled sensors. Using this data, factory managers may pinpoint processes that use a lot of energy and find ways to improve them. A factory, for instance, may change its production plan to run heavy machinery during off-peak hours, when energy costs are lower, based on insights provided by the IIoT.
Systems for the Management of Energy Automation:
One common feature of smart factories is the automation of energy management systems (EMS). Utilizing IIoT data, these systems may make real-time adjustments to lighting, heating, cooling, and equipment utilization. To save energy during idle periods, HVAC systems can, for example, regulate the temperature in some parts of the plant autonomously based on the amount of activity there.
Demand Response and Smart Grids:
Connecting smart factories to smart grids is a strategy for improving energy efficiency in the future. By leveraging IIoT technologies, smart grids are able to dynamically balance the supply and demand for electricity. During peak hours, factories that are linked to smart grids can engage in demand response programs, which allow them to lower their electricity prices by reducing energy use. The energy grid is stabilized, and expenses are reduced as a result.
Future Directions in Smart Manufacturing and Energy Conservation
Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Energy Optimization:
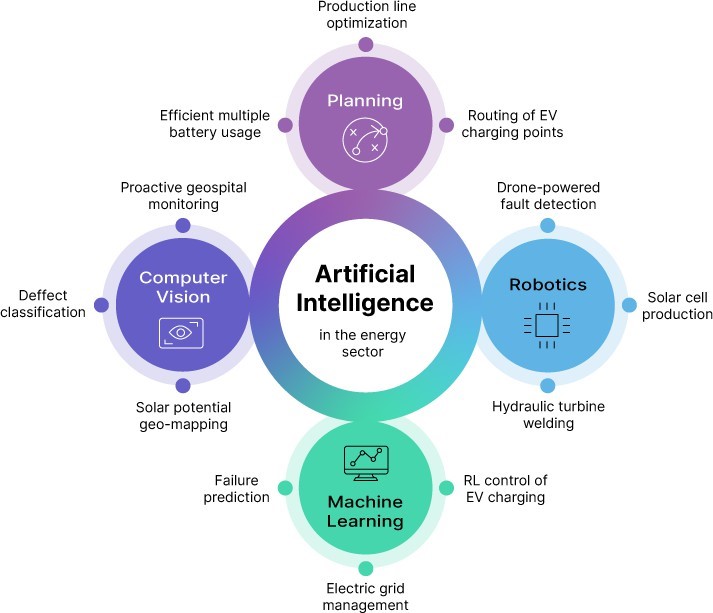
Smart factories will becoming more self-sufficient as IIoT and AI develop further. In order to learn how to become more energy efficient over time, AI algorithms can sift through enormous statistics collected by IIoT sensors. Machine learning algorithms can analyze past data and project future production demands to determine, for instance, how much energy should be used optimally.
Decentralized Energy Systems:
Embracing decentralized energy systems is a likely feature of future smart factories. Part of this process involves making use of energy storage devices, wind turbines, solar panels, and other renewable power sources. Using IIoT, factories can maximize energy efficiency by controlling when and how much electricity is drawn from renewable sources or local storage systems, thus decreasing their dependency on traditional power grids.
Improved Decision-Making with 5G and Edge Computing

IIoT in smart factories will undergo a radical transformation with the advent of 5G networks and edge computing. With the help of edge computing, data may be processed more quickly at the machine level, which in turn reduces decision-making latency. Factories will immediately save energy with 5G’s high-speed connectivity and more efficient data collection and processing.
Obstacles and Things to Think About
Smart factories have enormous potential benefits, but there are also certain obstacles to think about:
• Cybersecurity:
With the proliferation of IIoT-connected devices comes a heightened danger of cyberattacks; thus, smart factories must establish stringent security protocols to safeguard vital information and infrastructure.

• Upfront Costs:
Investing heavily in IIoT infrastructure, hardware, and software is necessary to transition to a smart factory, which comes with large upfront costs. The upfront cost may be high, but the energy savings and productivity gains in the long run usually make up for it.
• Workforce Training:
In order to run and oversee IIoT systems efficiently, it is necessary to train the workforce. To achieve this goal, it may be necessary to retrain employees to use new technology and comprehend the reasoning behind data-driven decisions.
Conclusion: The Future of Manufacturing
The industrial sector is undergoing a dramatic transformation as a result of the integration of IIoT with energy efficiency. Sustainable, flexible, and economically viable manufacturing systems are on the rise, and smart factories are at the forefront of this movement. Manufacturers may achieve their sustainability goals, boost production, cut costs, and optimize energy use with the help of IIoT. A number of promising developments, such as the integration of renewable energy sources, edge computing, artificial intelligence, and 5G, bode well for the future of smart factories and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Energy efficiency will continue to play a pivotal role in driving this change as technology advances, guaranteeing that future factories will be more intelligent, environmentally friendly, and efficient than previous ones.

Deepak Makraiya
Technical Lead – IoT
As a Technical Lead – IoT with over 8.3 years of experience, Deepak Makraiya specializes in Industrial Automation, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Cloud Computing, and AIoT.His expertise lies in designing and implementing cutting-edge IoT solutions, driving digital transformation for industries. With a strong focus on scalable cloud architectures and AI-powered IoT ecosystems, Deepak is passionate about leveraging technology to optimize processes, enhance productivity, and unlock business value in the industrial sector.












 sales@solutionanalysts.com
sales@solutionanalysts.com solution.analysts
solution.analysts






