
Table of Contents
The success of a project hinges on selecting the appropriate communication technology, especially as the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand. Long-range connection for Internet of Things (IoT) devices is provided by two prominent Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technologies: LoRaWAN and NB-IoT. Although they are both designed for low-power, wide-area communication, their individual characteristics make them more suited to specific applications.
If you’re trying to decide between LoRaWAN and NB-IoT for your Internet of Things project, this blog will walk you through the main points of each protocol, including their advantages, disadvantages, and potential uses.
| Key Differences | LoRaWAN | NB-IoT |
|---|---|---|
| Description | LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is an LPWAN protocol built on LoRa technology, enabling long-range communication between IoT devices over unlicensed frequency bands. It is highly energy-efficient, making it ideal for applications where devices need to operate on battery power for years. | NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT) is a cellular-based LPWAN technology that operates on licensed frequency bands. It offers secure, reliable coverage through existing cellular networks, making it ideal for large-scale IoT deployments. |
| Key Features | • Low power consumption: Suitable for battery-powered devices that need to last years without maintenance.
• Long range: Can cover distances of up to 15 km in rural areas. • Operates on unlicensed frequency bands: No licensing costs, but may face interference in crowded environments. • Star network architecture: Devices communicate directly with gateways, which then forward data to the cloud. |
• Licensed spectrum: Operates on secure and dedicated frequency bands, reducing interference.
• High coverage: Can penetrate deep indoors and provide consistent coverage in urban areas. • Low data rates: Supports small, infrequent data transmissions typical of IoT devices. • Cellular infrastructure: Leverages existing cellular networks, ensuring reliability and easy scaling. |
| Use Case | LoRaWAN is ideal for smart agriculture, environmental monitoring, and remote sensor applications where long-range communication and low power consumption are critical. | NB-IoT is well-suited for smart metering, asset tracking, and urban IoT deployments where coverage and security are key concerns. |
| Range | LoRaWAN offers extended range capabilities, reaching up to 15 km in rural areas, making it a great option for applications that need wide coverage in remote regions. | NB-IoT has a shorter range but excels in urban environments and offers excellent indoor penetration, making it ideal for city-based applications. |
| Power Consumption | LoRaWAN is known for its ultra-low power consumption, enabling devices to operate for years on a single battery | NB-IoT also offers low power consumption, but because it relies on cellular infrastructure, it may require more energy compared to LoRaWAN in some deployments. |
| Spectrum | LoRaWAN operates on unlicensed spectrum (e.g., ISM bands), which makes it cost-effective but susceptible to interference. | NB-IoT uses licensed cellular spectrum, providing more reliable and secure communication, but with the added cost of spectrum licensing. |
| Data Rate | LoRaWAN is designed for low data rates, typically supporting small payloads of data such as sensor readings. | NB-IoT offers slightly higher data rates and is more suited for applications that require periodic transmission of small to medium-sized data packets. |
| Network Architecture | LoRaWAN uses a star-of-stars topology where multiple end devices communicate with a gateway that forwards data to the cloud. | NB-IoT relies on a cellular-based infrastructure, where each device connects to a base station within the mobile network. |
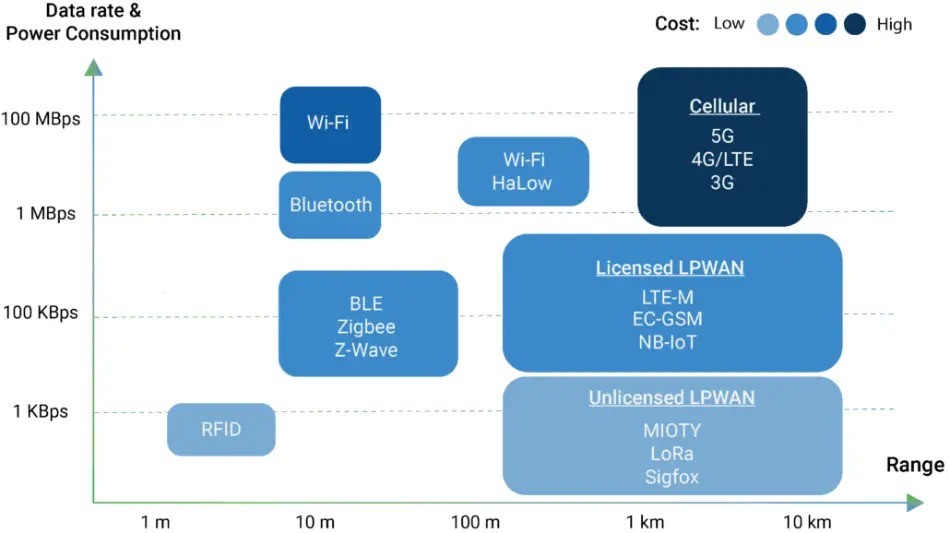
Deciding Between NB-IoT and LoRaWAN
Which of LoRaWAN and NB-IoT is better for your Internet of Things project is dependent on its unique requirements:
• LoRaWAN is a great option if you’re looking for a cheap solution that can communicate over vast distances while using very little power and operating on unlicensed spectrum. In places where cell phone service is spotty at best, this is a lifesaver.
• To provide constant coverage in densely populated locations and ensure safe, dependable connectivity, NB-IoT is the way to go. The licensed spectrum and cellular infrastructure of NB-IoT make it the best solution for device deployment in crowded areas like smart cities.
Conclusion
Both LoRaWAN and NB-IoT are strong LPWAN technologies, however they have different advantages and disadvantages. LoRaWAN’s low power consumption and long range make it ideal for distant and rural locations, but NB-IoT’s secure and reliable transmission across licensed spectrum makes it ideal for metropolitan areas. Considerations like range, power consumption, and network coverage should guide your technology selection for your Internet of Things project.
Your Internet of Things (IoT) implementation will be a smashing success if you take the time to learn about the two technologies and their respective advantages and disadvantages.

Deepak Makraiya
Technical Lead – IoT
As a Technical Lead – IoT with over 8.3 years of experience, Deepak Makraiya specializes in Industrial Automation, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Cloud Computing, and AIoT.His expertise lies in designing and implementing cutting-edge IoT solutions, driving digital transformation for industries. With a strong focus on scalable cloud architectures and AI-powered IoT ecosystems, Deepak is passionate about leveraging technology to optimize processes, enhance productivity, and unlock business value in the industrial sector.











 sales@solutionanalysts.com
sales@solutionanalysts.com solution.analysts
solution.analysts






