
Table of Contents
By facilitating device-to-device and cloud-to-cloud communication, the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing many sectors and making the dream of fully integrated systems a reality. Protocols and gateways for the Internet of Things are essential to this ecosystem because they permit devices and systems to communicate with one another without any hitches. Internet of Things (IoT) gateways connect devices to the cloud, and protocols specify how data is exchanged.
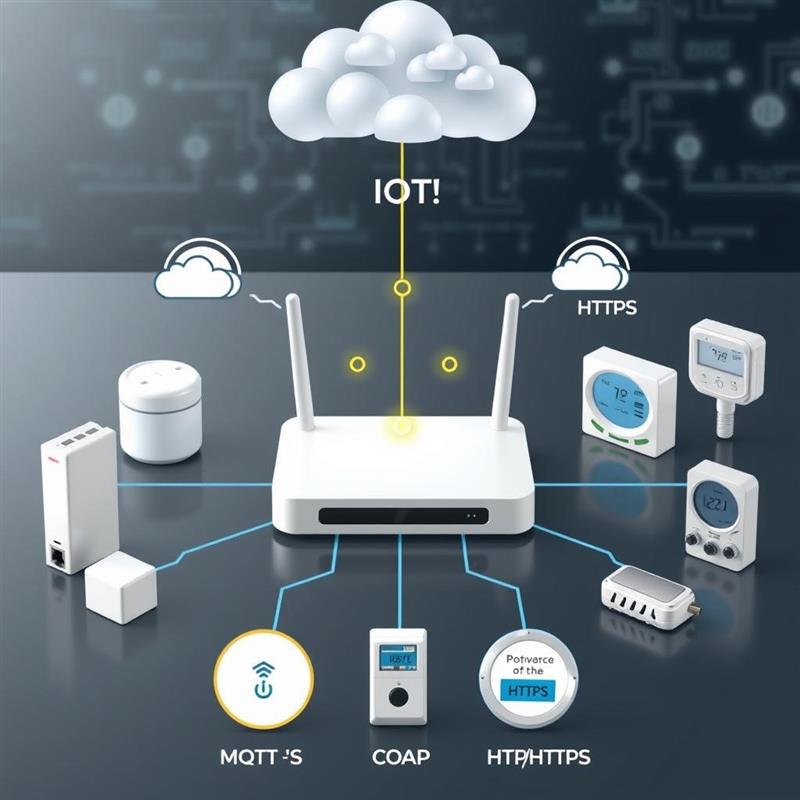
Internet of Things Gateways: What Are They?
Connecting sensors, actuators, and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices to remote servers in the cloud or on-premises is the primary function of an IoT gateway. Among its many functions is the management of data transfer between the device network and the cloud platform.
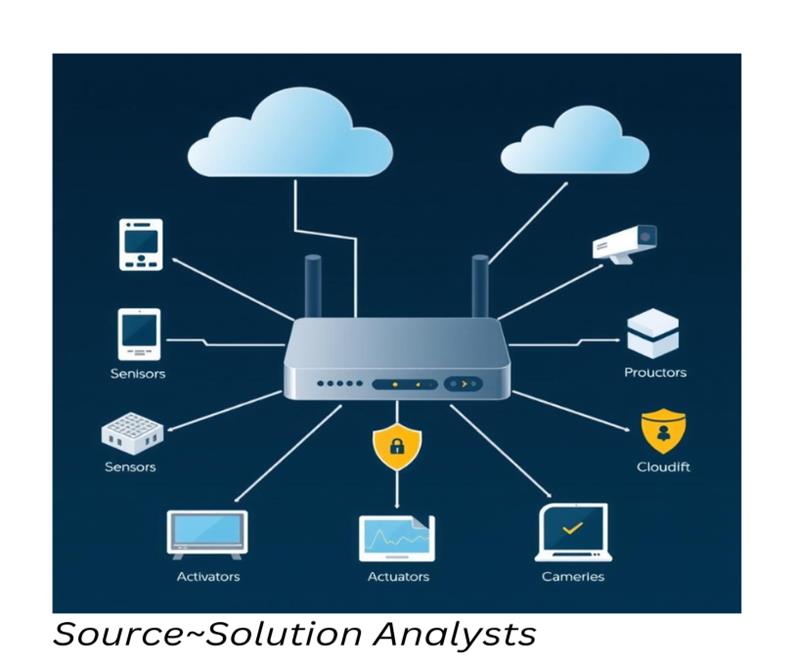
- Data conversion from protocols particular to devices to protocols that are compatible with the cloud is known as protocol translation.
- Prior to uploading data to the cloud, it undergoes data filtering and aggregation to remove any extraneous information.
- Encryption and authentication procedures are put in place to safeguard data while it is in transit.
- Processing data locally, at the edge, instead of constantly connecting to the cloud, is known as edge processing.
Example: An Internet of Things (IoT) gateway, for instance, can coordinate the flow of data from various smart home devices, such as smart lights, security systems, and thermostats, and transmit the most pertinent information to a cloud service for processing or action. This communication is made easy and safe by Internet of Things gateways and protocols
Step 1: One Must First Select an Appropriate IoT Gateway
A number of criteria, including the nature of the IoT devices, the surrounding environment, and the volume of data, must be considered when choosing an appropriate IoT gateway.
The two most common kinds of gateways are:
- Before transmitting data to the cloud, edge gateways process and make decisions locally. Perfect for use in real-time scenarios.
- Cloud Gateways: Their main goal is to transmit unprocessed data to the cloud.
Considerations:
- Hardware compatibility: Make that the gateway is compatible with the protocols used by your Internet of Things devices, such as Zigbee or Z-Wave.
- Network: Pick gateways that have the right network capabilities, like Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or cellular.
- To be sure your gateway can keep up with your expanding Internet of Things network, consider its scalability.
Ensuring the seamless flow of data is crucial for the efficacy of IoT gateways and protocols, and the proper gateway plays a critical role in this.
Step 2: IoT Protocols Overview
The second step is to have an overview of IoT protocols. In order for IoT ecosystems to communicate efficiently, IoT gateways and protocols are crucial. Devices’ interactions with gateways and cloud services are defined by protocols. Here are the top protocols for the Internet of Things:
- The Message Queuing Telemetry Transport protocol
For low-bandwidth, high-latency settings, there is a lightweight messaging protocol called MQTT. It has many uses in the IoT and is utilized for transmitting data in small packets.
Key Characteristics:
- Devices (the publishers) transmit data to a broker, who in turn distributes it to the subscribers, in the publish-subscribe model.
- Perfect for gadgets that run on batteries because of its low power consumption.
- MQTT allows for encryption using TLS/SSL, which enhances security.
Use Case: Smart agricultural systems that monitor soil moisture and temperature with periodic sensor readings are one such application.
- The Restricted Application Protocol, or CoAP
For devices with little resources and low power consumption, there is a web-based protocol called CoAP. The REST model serves as its foundation, and basic operations like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE are supported.
Notable Characteristics:
- Compact: Communicates with little overhead by utilizing UDP.
- Easy integration with web-based systems: RESTful API.
- Smart meters and other low-energy devices benefit from this feature because of its low power consumption.
Use Case: CoAP finds widespread application in smart lighting systems due to its emphasis on energy efficiency.
- Secure and HTTP
Internet of Things (IoT) applications that necessitate strong security and broad interoperability still employ HTTP/HTTPS, despite the fact that other protocols are better suited for this purpose. For situations when devices must interact with web servers directly, it is of great assistance.
Important Features:
- Compatible with Preexisting Web Infrastructure: Offers a standardized experience.
- Protected: Communication is made secure via HTTPS.
- Excessive overhead: Not ideal for energy-efficient Internet of Things devices.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices that require direct connection to cloud servers, such as streaming devices or cameras, are prime examples of this use case.
- Z-Wave and Zigbee
Two low-power wireless protocols developed for use in home automation and local device communication are Zigbee and Z-Wave.
Key Features:
- Mesh networking is a key feature since it reduces the need for a central hub by allowing devices to connect directly with each other.
- Low power consumption: Designed to extend the life of devices that rely on batteries.
- Zigbee (10-100m) and Z-Wave (up to 30m) are applicable here.
Use Case: Incorporated into thermostats, lights, and locks that are part of smart home systems.
Step 3: connect IoT gateways to cloud services.
Connecting your Internet of Things devices to a gateway is the first step in sending data to a cloud service for analysis and storage. Integrating with Internet of Things (IoT) gateways and protocols is a breeze on most cloud platforms, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Procedures:
- Configure an Internet of Things service (such as AWS IoT Core) to receive and handle data sent by your gateway.
- To transfer data to the cloud, configure the gateway to utilize the appropriate protocol, such as MQTT or HTTPS.
- Process and view the data in real-time with the help of analytics services on the cloud.
Step 4: Manage Data and Process at the Edge
Internet of Things (IoT) gateways and protocols with edge processing capabilities are becoming more important as IoT systems expand. By handling data locally, edge processing decreases bandwidth utilization, enhances security, and decreases latency.
Edge Processing’s Advantages:
- Applications requiring instantaneous choices (such as industrial automation) necessitate reduced latency.
- Data processing locally reduces bandwidth utilization by sending only essential data to the cloud.
- The ability to handle sensitive data locally before uploading it to the cloud improves security.
For instance, in a manufacturing environment, an edge gateway can analyze vibration data from machinery to identify irregularities, immediately turn off the gear, and then transmit comprehensive findings to the cloud.
Step 5: Validating the Security of the IoT Gateway
Internet of Things (IoT) network security is paramount, particularly for large-scale implementations. The primary function of Internet of Things (IoT) gateways and protocols is to restrict network access to only authorized, secure data.
Recommendations:
- Make sure that all communications between devices, gateways, and cloud platforms are encrypted using TLS or SSL.
- Take precautions against cyber dangers by setting up intrusion detection systems and firewalls.
- Make that all of your linked devices use robust authentication methods, such certificate-based authentication.
Conclusion:
Internet of Things (IoT) gateways and protocols guarantee dependable, secure, and scalable communication between devices and the cloud, which is essential for successful IoT deployments. Your Internet of Things (IoT) solution can be optimized for speed, safety, and scalability by learning about gateways’ functions and using the correct protocols.
Staying ahead in the ever-changing landscape of connected devices will need mastery of gateways and protocols as the Internet of Things (IoT) grows.

Deepak Makraiya
Technical Lead – IoT
As a Technical Lead – IoT with over 8.3 years of experience, Deepak Makraiya specializes in Industrial Automation, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Cloud Computing, and AIoT.His expertise lies in designing and implementing cutting-edge IoT solutions, driving digital transformation for industries. With a strong focus on scalable cloud architectures and AI-powered IoT ecosystems, Deepak is passionate about leveraging technology to optimize processes, enhance productivity, and unlock business value in the industrial sector.











 sales@solutionanalysts.com
sales@solutionanalysts.com solution.analysts
solution.analysts






